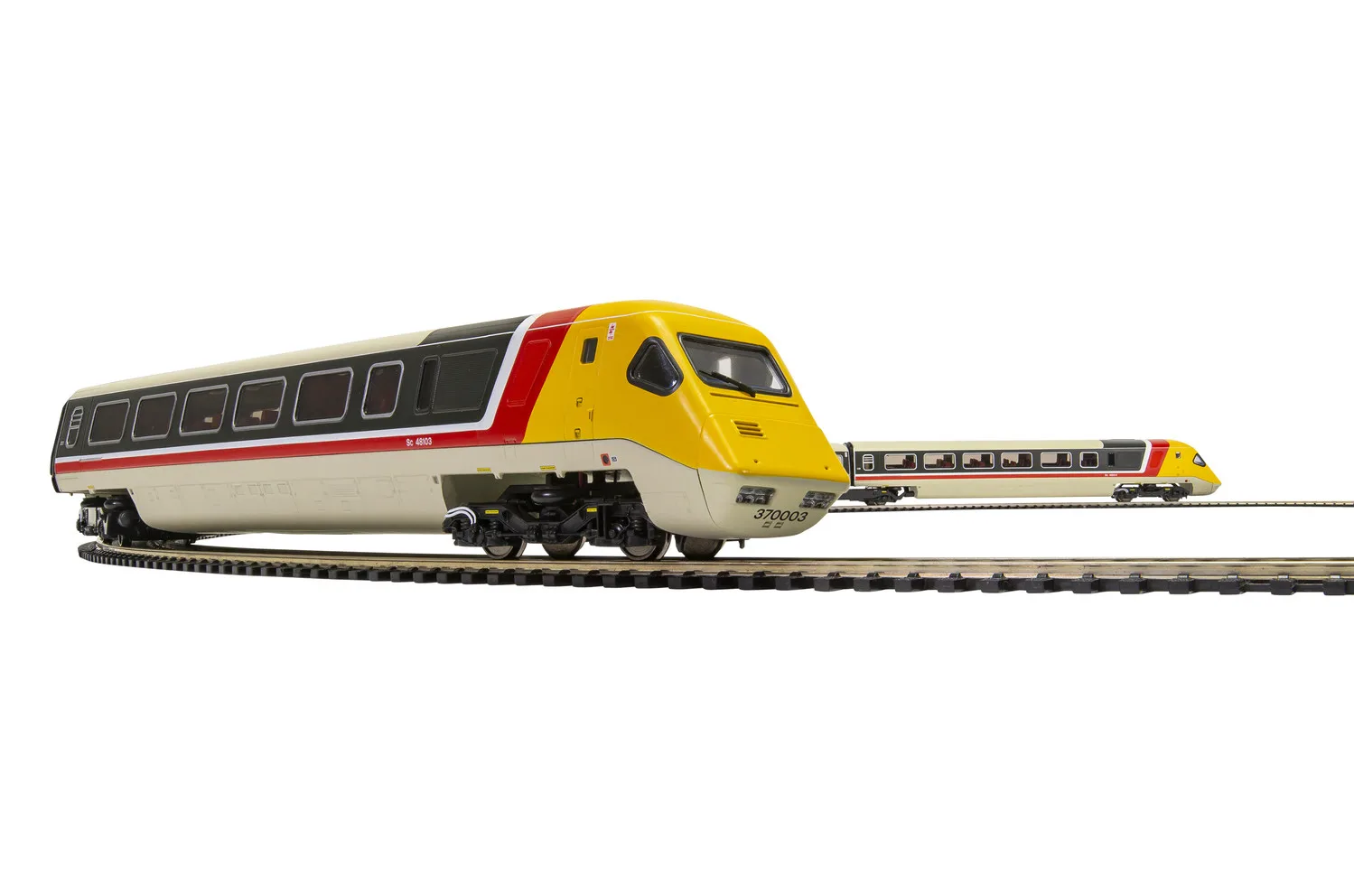
BR, Class 370 Advanced Passenger Train, Sets 370 003 and 370 004, 5-car pack – Era 7
British Rail Class 370 Advanced Passenger Train 5-car Pack Set 370 003 comprising DTS Sc48103, TBF Sc48603 and NDM Sc49003 City of Derby, along with Set 370 004 comprising TBF Sc48604 and DTS Sc48104. By the end of 1970 the British Rail Board began considering the third design phase of the Advanced Passenger Train; the prototype for the full production trains that would incorporate the technology of the APT-E in a practical application.
From the outset the pre-production APT project, or APT-P, was considered to be nothing more than a proving prototype for evaluation, prior to the finalized Advance Passenger Train design being authorized for squadron service; the APT-S. Having settled on electric traction for the production APT, the West Coast main line between Euston and Glasgow was the obvious route for conducting testing, being electrified along its length and with some severe curves that curtailed high speed travel. The date for commencement of services was set for 1977 and the Chief Mechanical and Electrical Engineers’ Department (CM&EE) design engineers began work in October 1973. In a move similar to the current situation of the DfT defining design specifications, it was the passenger business of British Rail that decided upon the original configuration for the APT-P. Each set was to comprise fourteen cars, with the two power cars marshalled at the outer ends of the sets.
It soon became clear that the use of two pantographs, one on each power car, was unsuitable for the OHP wires in place at that time and the use of two power cars in the middle of the train became the only option, effectively cutting the train in half. This created two 1+6 formations of DTS, TS, TRBS, TU, TF, TBF and NDM (Non-Driving Motor), through which passengers could not pass due to the high magnetic fields generated by the electrical equipment contained in the NDM. The NDM was the first vehicle completed for testing in June 1977 and it spent a year on static tests at RTC Derby, as well as dynamic tests on the WCML with a spare HST Power Car from September 1977.
In mid-1978 the power car was joined by the rest of the first half set for testing on the WCML and was unveiled to the press on June 7th but, hampered by industrial action, it was to be February 1979 before various formations of the full train were marshalled to test different aspects of the train. At the end of the year on December 20, 1979, a new rail speed record of 162.2mph was achieved and by March 1980 all three APT-P trains were delivered and ready for mileage accumulation on the WCML.
Having finally achieved full route clearance and with testing indicating that all was progressing to plan, shadow passenger service was set to commence on June 9, 1980 with a daily Glasgow/London return service. A demonstration run on April 18th with a 1+9 set was meant to usher in a new era of high speed rail travel, but a derailment caused by a faulty articulated bogie signaled the beginning of the APT ‘jinx’ and the postponement of passenger introduction. Wheelsets had to be rebuilt across the fleet and reliability problems with the tilt, transmission and braking systems were also exacerbated by the mediocre ride quality. It was also found that failure of the tilting mechanism could result in the APT exceeding its kinematic envelope and potentially coming into contact with an APT travelling in the opposite direction.
It was to be Spring 1981 before main line testing could resume and by now media and public opinion was turning against the project, with some individuals in Government and within the British Railways Board expressing their discontent as well. Entering public service on December 7, 1981 at first all went well, but very cold weather in Scotland on December 9th and again on December 11th resulted in the brakes freezing and the APT being taken out of traffic until the summer of 1982. A year of technical R&D project running followed, before limited passenger running took place across 1983/84 to assess passenger comfort using the full 2+12 sets between London Euston and Glasgow, culminating in a new time and speed record for the 401 mile trip of three hours and fifty-two minutes; an average speed of 103mph.
Far exceeding its budget, APT-P had now effectively reached the end of its development program. Although a number of plans had been suggested for the implementation of APT in service, in a number of formations and with varying traction options, the APT-S, APT-R, APT-T, APT-U and APT-V projects never materialized. The fleet of six sets had been reduced since March 1983, parts being canonicalized to keep the remaining vehicles running and at the end of May 1985 the